The Buzz and Fuss on Ketogenic Diet
Yasmin Laura Marie Zuñiga, MD, FPCP, PCEDM
By starving the body of carbohydrates and glucose, the body will then burn fat for energy, which promotes fat and weight loss.
It used to be believed that the best way to diet, i.e. to reduce weight, was to eat a low-fat or low carbohydrate diet, preferably with moderate to high protein intake. However, studies show that successful weight loss ultimately hinged on sustained calorie deficit – it didn’t really matter which macronutrient you cut down as long as you kept the calories off. Unfortunately, this is the ultimate struggle for many, especially during holiday season!
In recent years, a more appealing way to weight loss seems to have emerged. After all, who doesn’t want to lose weight without having to limit calories? Have we finally found the diet equivalent of the magic pill? Is this the Holy Grail for weight loss? Enter the ketogenic diet, also known as very low carbohydrate, high fat diet.
What exactly is a ketogenic diet?
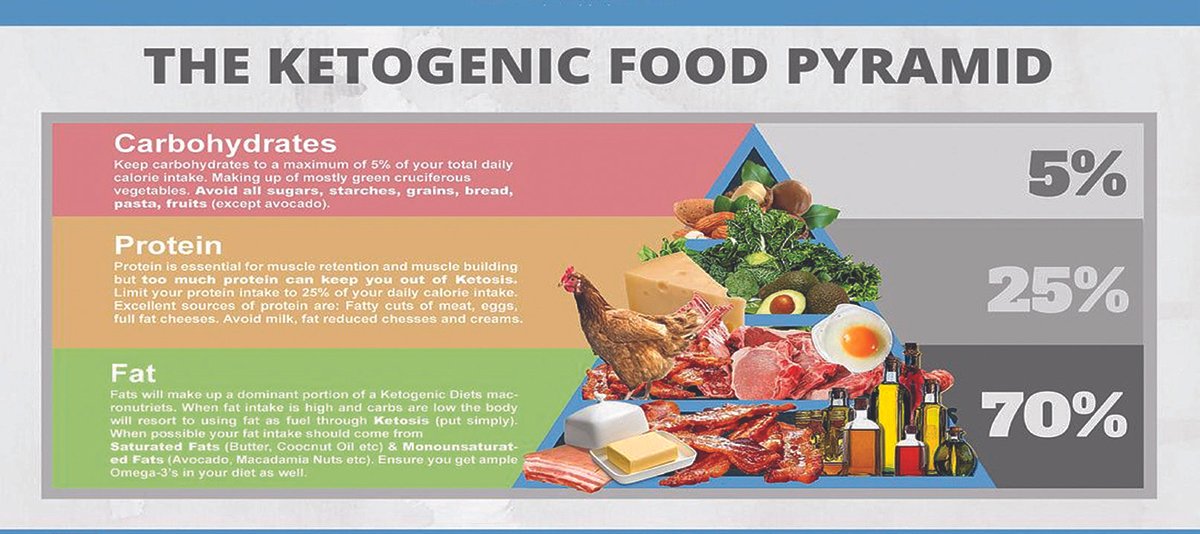
Ketogenic diet is a diet that aims to increase the level of circulating ketones in the body, which places the person under a state of physiologic or nutritional ketosis. Aside from complete fasting, such a state is attained by restricting carbohydrates to a maximum of 50 grams daily (~200 calories), while keeping the protein to a moderate amount (~1.2-1.5 grams/kilogram/day), with the remaining 60-80% of total calories coming from fat. This translates to a very low carb, high fat and moderate protein diet. By “starving” the body of carbohydrates and glucose, the body will then burn fat for energy, which promotes fat and weight loss.
Are ketosis and ketoacidosis one and the same?
Ketosis is different from a ketoacidosis state, wherein a dangerous overproduction of ketone bodies occurs due to the absence of insulin and is associated with elevated blood glucose levels. Due to very low carbohydrate intake, this is unlikely to occur in the ketosis state.
When is ketogenic diet useful?
Before its weight loss potential, ketogenic diet was originally used as early as the 1920s for intractable childhood epilepsy, where ketone bodies had a neuro protective effect by modifying the way brain cells utilize energy.
What are the benefits of ketogenic diet?
One of ketogenic diet’s main advantages is that despite eating high calories, there is consistent body fat and body weight loss, including suppression of hunger. Studies suggest that either the ketone bodies directly suppress appetite, or the high protein intake keeps one full. Some experts think that using protein as an energy source is an “expensive” process for the body, which then leads to a “waste of calories” and increased weight loss.
On top of weight loss, other benefits include lower diastolic blood pressure and improved cholesterol profile (reduced total cholesterol and triglycerides and increased HDL levels), although some studies mention increased bad cholesterol (LDL) levels for those on ketogenic diets for more than 12 months. Diabetes control appears to improve, possibly leading to reduced medication doses.
Will there be a yoyo effect when I am on ketogenic diet?
Many studies show that people lost more weight with the ketogenic diet vs. low fat diets, at least in the short term. The best measure of success, however, would be whether at least 10% of body weight is kept off for at least a year. To avoid any yoyo effect on weight, experts recommend doing two (2) brief periods of ketogenic diet separated by longer periods of the Mediterranean diet.
Is ketogenic diet for everyone? Is it safe?
Ketogenic diet may be used safely by obese individuals for a limited period: a minimum of 2-3 weeks up to a maximum of 6-12 months, to stimulate fat loss and improve metabolism with the end goal of transitioning to a correct diet style over long-term, preferably the Mediterranean diet.
The use of ketogenic diet allows flexibility in the use of long-chain and medium- chain triglycerides. No specific fluid requirements have been mentioned. Here are the recommended laboratory workups for monitoring:
Glucose, albumin, total protein, lipid profile, creatinine every 3 months
Yearly kidney and urinary bladder ultrasound, bone mineral densitometry, 12L ECG, echocardiogram
Are there side effects?
Short-term side effects include nausea, vomiting, constipation, dehydration, loss of appetite, weakness, and even bad breath, mainly from cutting out carbs and from lower fiber intake. In the long term, ketogenic diet may lead to fatty liver disease, cardiomyopathy (the heart not pumping well) and elevated bad cholesterol levels from high intake of saturated fat. Osteoporosis and kidney stones are also possible long-term complications. That said, people with kidney issues (stones, chronic kidney disease, post-kidney transplant) and those with reflux symptoms (gastrointestinal reflux disease or GERD) are advised not to do this diet for weight loss. Word of caution for those with diabetes: medication dose adjustments may be required especially for those on insulin, to avoid hypoglycemia.
The Last Word
Most of the studies involving ketogenic diet were done on short-term basis, with a maximum of 12 months. Because this diet is lopsided to favor fat intake compared to standard diets, prior to starting, physician and nutritionist – dietician consultations are must-do. Use of this diet must be guided and supervised by a nutritionist dietician, with regular monitoring of blood parameters by your physician. While weight loss is important and may be the initial goal, one must not lose sight of the big picture, that is, to transition into and maintain a healthy eating pattern for overall health.
Sources: Gupta L. et al. J Postgrad Med 2017; 63:242-251. Wing RR et al. Annu Rev Nutr 2001; 21:323-341. Hashimoto et al. Impact of low-carbohydrate diet on body composition: meta-analysis of randomized controlled studies. Obes Rev 2016; 17(6):499-509.
See more Endocrine Hotspots Editions at endo-society.org.ph/endocrine-hotspots
Brought to you by the Philippine College of Endocrinology Diabetes and Metabolism (PCEDM)
Website: endo-society.org.ph
IG: @endocsociety
Twitter: @EndoSoc_ph
Facebook: fb.com/filipinoendocrinologists