What is GYNECOMASTIA (“Man Boobs”)?
Annette Chua, MD
What is Gynecomastia?
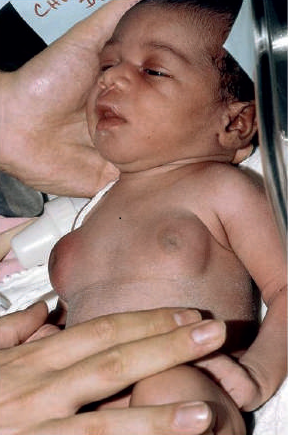
Gynecomastia is a condition wherein there is an increase or enlargement of the breast tissue in males. “Man boobs” or “moobs” are commonly used terms for gynecomastia, but they may also pertain to having excess fat in the chest area, not necessarily the breast glands.
What are the symptoms?
It can affect one or both breasts, sometimes unevenly. Other than the visibly enlarged breast tissue, a lump or swelling may be felt beneath the nipple that can also be painful to touch.
What causes it?
Gynecomastia may develop when there is an increased level of estrogen relative to the amount of testosterone. Estrogen is a hormone that promotes development of female physical traits including the growth of breast tissue. Both men and women have estrogen, however the levels are significantly less in men.
There are phases in the lifetime of a male when gynecomastia may naturally occur.
1.) After birth – in the first 2-3 weeks of infancy. This is due to the effect of the mother’s estrogen.
2.) During adolescent period – due to hormonal changes at puberty. This may go away without treatment in 6 months to 2 years; and
3.) At age 50 years old and above, as the production of testosterone declines.
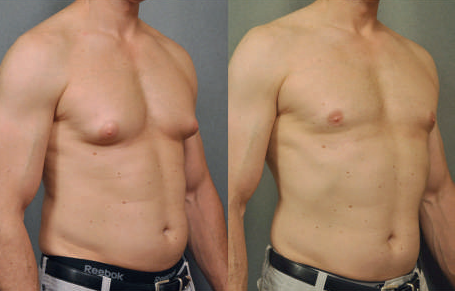
Should you see a doctor?
• It is important to see the doctor for proper medical evaluation. There are conditions that may appear similar to gynecomastia. Excess fat around the breast are common in overweight or obese individuals but they don’t truly have enlarged breast glands. More serious conditions such as abscess or even breast cancer can also occur in men hence must be ruled out.
• Gynecomastia may be due to medical conditions that disrupt the hormonal balance such as hypogonadism (low production of testosterone by the testes), kidney or liver failure, thyroid dysfunction and malnutrition.
• A wide range of medications can also cause gynecomastia such as: antiandrogens, some anti-anxiety drugs, antidepressants, antibiotics, certain ulcer and stomach motility medications. Even intake of androgens (male hormones) and anabolic steroids used in bodybuilding may paradoxically increase the risk of developing gynecomastia.
• Alcohol and illicit drugs such as marijuana, heroine and amphetamines are among other causes.
• Some herbal products or plant oils used in shampoos, soap and lotions have also been associated with gynecomastia.

Karyotype 47, XXY
What are the tests for gynecomastia?
Gynecomastia can be usually diagnosed by careful examination of the breast by your doctor. A comprehensive physical examination can help uncover underlying medical conditions. Initial tests may include blood tests and mammogram. Depending on the impression and initial results, additional tests may be necessary.
How is it treated?
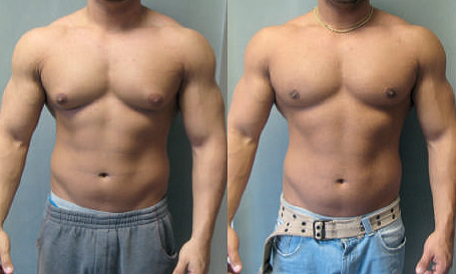
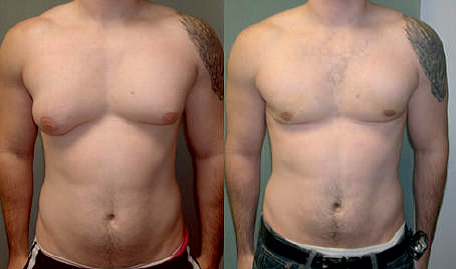
Most cases of gynecomastia, especially those that occur during adolescent, resolve over time without treatment. Gynecomastia usually resolves with treatment of the underlying medical condition or stopping the offending drug.
Although the gynecomastia itself does not cause physical danger, it may cause significant psychological distress or embarrassment because of its appearance. Treatment may be necessary if gynecomastia doesn’t improve on its own or if it causes significant pain, tenderness or embarrassment. Medications used in hormone therapy for patients with breast cancer, tamoxifen and aromatase inhibitors, may be helpful.
If enlarged breast tissue persists after initial treatment and is significantly bothersome, surgery to reduce the excess tissue is sometimes recommended.
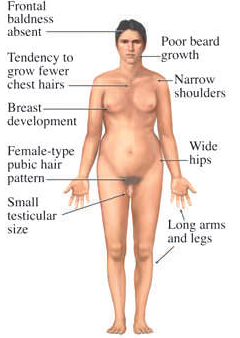
Klinefelter Syndrome
What is GYNECOMASTIA (Man Boobs)?
Annette Chua, MD
Part of the March 2020 Endocrine Hotspots Edition
See our other Endocrine Hotspots Edition
Brought to you by the Philippine College of Endocrinology Diabetes and Metabolism (PCEDM)
Website: endo-society.org.ph
IG: @endocsociety
Twitter: @EndoSoc_ph
Facebook: fb.com/filipinoendocrinologists